Compliance in Healthcare: Navigating Regulatory Changes and Their Impact
Let’s have a conversation
Healthcare faces constant scrutiny due to ever-changing industry regulations. Healthcare compliance necessitates adherence to ethical, legal and professional standards. These regulations increase patient and consumer safety by preventing abuse, fraud and waste. A strong culture of compliance is a proactive and continuous commitment to not only meeting regulatory requirements but also safeguarding the organization’s reputation and fostering ethical conduct.
Healthcare providers and insurers must stay ahead of evolving regulations and develop strong compliance strategies. Noncompliance can result in penalties, license revocation, sanctions, business cessation and patient and consumer risks.
This guide explores key regulatory changes and how organizations can ensure compliance.

The Importance of Regulatory Compliance in the Healthcare Industry
Regulatory compliance in healthcare is essential because it ensures safe, quality patient care. Healthcare regulations apply to all healthcare enterprises, including hospitals, practices, insurers and pharmacies. Complying with healthcare regulations is critical for the following reasons:
- Avoids legal risks: Healthcare organizations must adhere to local, state and federal laws. Legal violations can lead to patient lawsuits or imprisonment.
- Improves patient care: Regulations set safety and infection control measures for patient safety.
- Ensures protected health information (PHI): Medical records contain patients' sensitive data. Healthcare institutions must follow privacy and security standards to prevent unauthorized access.
- Enhances reputation: Adhering to best practices enhances an organization's trustworthiness and reputation.
- Prevents financial loss: The cost of noncompliance is higher than imposed fines. Sanctions or license revocation can cause service disruption that impacts revenue.
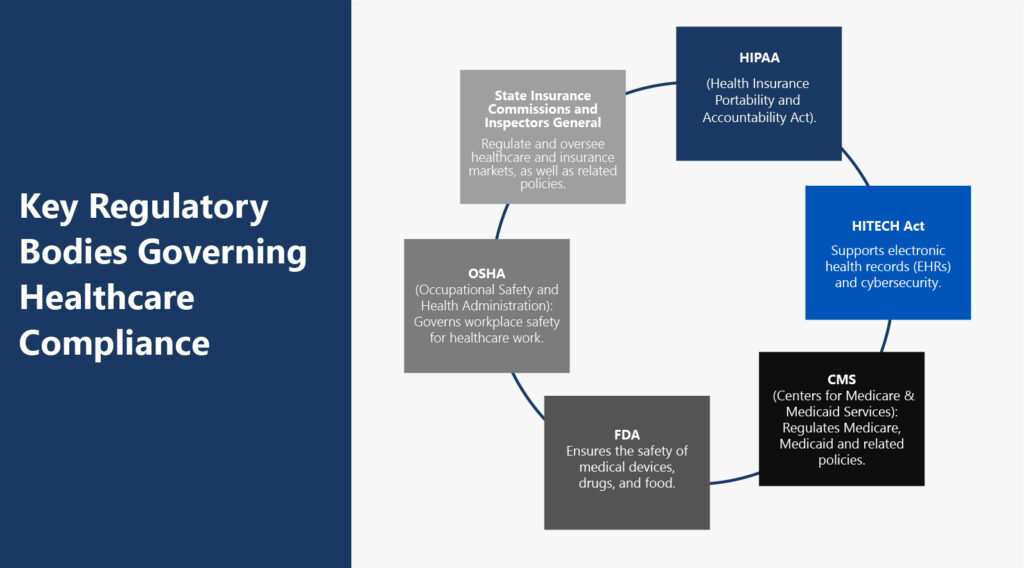
Significant Healthcare Regulatory Bodies
Key regulatory bodies govern healthcare industry standards. These include the following:
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA): The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) established HIPAA to legislate standards for protecting sensitive health information. HIPAA's Privacy Rule prohibits the disclosure of PHI without patient consent.
- Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act: This act is part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA). It incentivizes providers to adopt electronic health records (EHRs). The act requires healthcare organizations to report data breaches in support of HIPAA's Privacy Rule.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): Regulates Medicare, Medicaid and related policies.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Ensures the safety of medical devices, drugs, and food.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA governs safe and healthy working conditions for healthcare workers and other employees. Healthcare workers face unique safety hazards. OSHA enforces standards around biological waste, chemical exposure and bloodborne pathogens.
- State Insurance Commissions and Inspectors General regulate and oversee healthcare and insurance markets, as well as related policies, to enhance the efficiency and integrity of healthcare programs.
Fundamental Regulatory Changes Affecting Healthcare Organizations
Recent changes in healthcare regulations address healthcare transactions. Many changes in the first quarter of 2024 focused on healthcare transactions. Noteworthy developments include:
Transaction Review Laws
States have adopted healthcare transaction legislation on access, quality, competition and need impacts. The definition of “material transactions” may differ depending on the state.
Healthcare transaction review laws require:
- Prior approval for some transactions based on due diligence.
- Long timelines for the relevant bodies to review transactions.
- Consideration of proposed transaction cost, competition, access and equity.
- Transparency on all aspects of a healthcare transaction, including divulging all parties involved.
CMS Broker Rule and 80/20 Rule
In April 2024, CMS published the Medicare Advantage and Part D Final Rule. The rule increased guardrails in many programs, including the Medicare Advantage and Cost Plan. Part of the rule included a cap on broker compensation. This limit prevents brokers from guiding patients to specific plans for financial incentives.
CMS released the Ensuring Access to Medicaid Services Final Rule. The rule states that 80% of Medicaid payments for home health services must go to care workers instead of overheads or profit.
Laboratory-Developed Tests Final Rule
Another legislative release in April 2024 was the FDA's final rule on laboratory-developed tests (LDTs). LDTs are diagnostic tests developed and validated in-house by laboratories. The regulation amends in vitro diagnostic (IVD) products to fall under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic (FD&C) Act. This amendment phases out the FDA's previous approach of discretion. It aims to ensure that LDTs are safe and effective for clinical use.
Evolving Telehealth Regulations
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth has shifted from a secondary to a primary healthcare choice. Regulations have risen to meet this shift:
- Service expansion: Congress passed the Preserving Telehealth, Hospital and Ambulance Access Act (H.R. 8261), extending telehealth services through 2026.
- Payment parity: Some states require insurers to reimburse telehealth at the same rate as in-person visits. This differs from service parity, which requires the same services for in-person and telehealth.
- Licensure: States have specific regulations for providing telehealth services across state lines. Some, such as California, have exceptions, such as treatment for life-threatening illnesses. Other states, like Florida, have registration processes for external providers.
- FDA guidelines: The FDA established regulations on wearable patient monitoring devices and telehealth software.
Updates to Privacy and Security Rules
Proposed changes to HIPAA's Privacy Rule are imminent. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR) reviews and enforces HIPAA rules.
Here are some of the highlights of the proposed changes:
- Patients can view and take photos of their PHI in person.
- Covered entities may send electronic protected health information (ePHI) to personal health applications at a patient's request.
- Organizations must provide fee estimates for providing patients with PHI copies.
- “Healthcare operations” will expand to include case coordination and care management.
- Once published, organizations must update policies and train employees on new privacy laws.
Importance of Quality Metrics
It's easier for healthcare providers to report compliance using accurate quality measures. The Institute of Medicine (IOM) Quality Framework quantifies quality in six domains:
- Safe: Prioritizing patient safety in care and service delivery
- Effective: Allocating care to those who need it and refraining from misuse
- Patient-centered: Considering the patient's needs in all care decisions
- Timely: Preventing delays or lengthy wait times
- Efficient: Using resources in a way that avoids waste
- Equitable: Equal care provided regardless of demographics or socioeconomic status
These metrics help healthcare entities ensure quality and meet changing regulations.
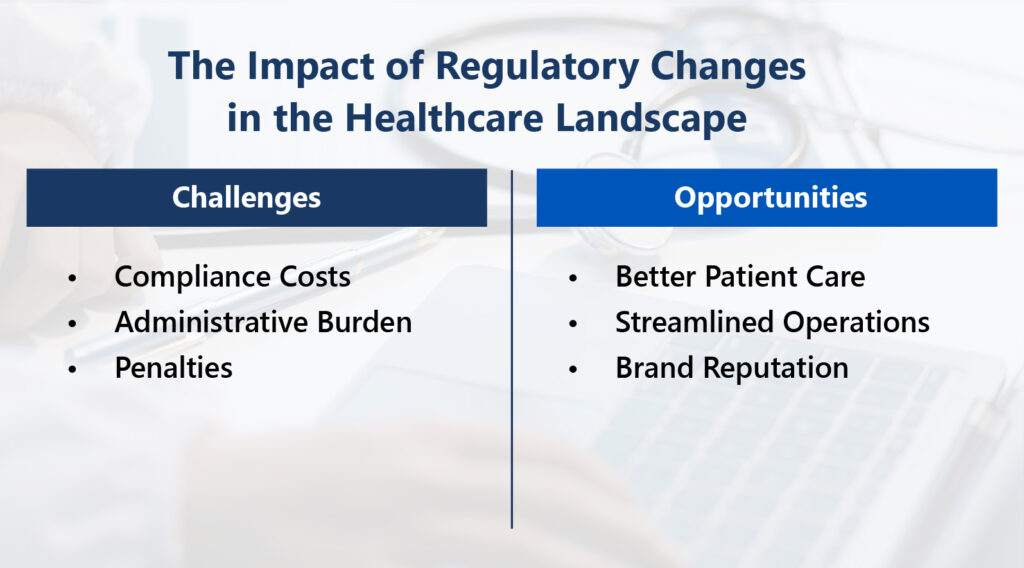
The Impact of Regulatory Changes in the Healthcare Landscape
Each regulatory change brings unique challenges and opportunities to healthcare. Organizations must adapt or risk noncompliance.
Challenges Posed by Changes
Shifting regulations can pose obstacles for healthcare providers, including:
- High compliance costs: Adapting to changing regulations can mean spending funds on new systems, training or data handling.
- Administrative burden: Updating policies, procedures or practices requires time and administrative effort.
- Service impact: Evolving healthcare standards can impact the services offered. The COVID-19 pandemic increased the use of telehealth and virtual consultations.
- Noncompliance penalties: Organizations may face fines or lost business due to brand damage.
- Pricing revisions: Regulations may require changes to pricing strategies. Healthcare organizations with Medicare patients must account for changing Medicare reimbursement rates.
- Increased risk management: New standards introduce compliance, financial and operational risks. The shift to value-based care models in the U.S. requires healthcare providers to prioritize care quality over volume.
- Staff training: Healthcare employees need ongoing training to keep updated with regulatory changes. Training involves costs and operational disruption.
- Technology adoption: Regulations mandate technologies like EHRs (HITECH) and data security measures (HIPAA). To comply, healthcare organizations must adopt these technologies. New systems come at an expense and require training.
Opportunities Created by Changes
If healthcare organizations can navigate the obstacles, changing regulations present significant opportunities:
- Improved patient care: Complying with regulations increases patient safety and satisfaction. Strict controls mean lower infection rates with better quality care.
- Enhanced data security: Data privacy laws lower breach risks, safeguarding patients and organizations. Security measures restrict unauthorized access.
- Competitive advantage: Effective compliance makes healthcare organizations stand out from competitors. Regulations level the playing field. Providers who use sneaky practices to win patients risk the consequences.
- Streamlined operations: Advanced healthcare technology can increase efficiency, boost productivity and reduce errors.
- New revenue opportunities: Expanding services can create additional revenue streams for practices.
- Increased brand reputation: Following compliance and ethical best practices enhances brand reputation. Compliant healthcare organizations that provide high-quality care gain more patient trust.
- Collaboration benefits: Regulations can foster partnerships with entities like EHR compliance-focused IT firms. These partnerships offer knowledge not available internally. Collaboration can open up new markets and make it easier to adapt to regulatory changes.
How to Create an Effective Compliance Program
A compliance program is a set of policies and processes to ensure healthcare organizations follow relevant laws. This program helps prevent, detect and correct regulatory noncompliance.
Follow these best practices for a successful compliance program:
1. Establish Procedures, Policies and Conduct Standards
The first step in creating a compliance program is identifying which regulations apply. The second step is evaluating the existing compliance measures. Following this assessment, formulate a plan to address any gaps. Policies and procedures establish guidelines for compliance. They should be straightforward, easy to understand and communicated to all staff. Below are examples of what to include:
- Compliance responsibilities: Outline roles for compliance officers, the compliance committee, management and staff.
- Program structure: Describe the program's operations, including reporting procedures, compliance resolutions and monitoring.
- Success measures: Determine methods to measure program effectiveness.
2. Assign a Compliance Officer and Committee
HIPAA regulations mandate healthcare providers to appoint a privacy officer. The compliance officer ensures the organization complies with internal and external standards. A compliance committee of individuals with diverse backgrounds supports the officer. The compliance officer and committee administer the program together. They should hold regular meetings to discuss regulation updates, reporting and compliance enforcement.
3. Train and Educate Staff
All healthcare staff must receive continuous training on compliance and regulatory updates. HIPAA's Privacy Rule mandates training staff on policies, procedures and security awareness. This education ensures staff and management understand expectations and codes of conduct. Any vendors or associated partners should also understand compliance standards.
4. Develop a Communication Strategy
Creating open channels of communication is essential for both top-down and bottom-up communication. This way, staff remain aware of regulation updates and can report compliance issues.
A strong communication plan should include:
- The process for reporting compliance issues.
- Methods for anonymous reporting, such as a hotline.
- A log for reported compliance issues.
5. Monitor and Audit
A healthcare compliance program doesn't mean automatic compliance. Regular program assessments ensure compliance with the relevant laws, rules and regulations. Monitoring and auditing serve different objectives:
- Monitoring: Internal reviews assess procedure effectiveness and identify potential issues. Problems uncovered while monitoring may lead to an audit for further investigation.
- Auditing: This process involves deep-diving into specific areas of concern and using measures to assess compliance. An audit looks into how or why issues occur.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Office of Inspector General (HHS-OIG) established a work plan indicating potential risks. Adding these areas can help organizations address HHS-OIG priority risks.
6. Enforce Standards Through Sanctions
Healthcare organizations must enforce compliance violations or noncompliant behavior through appropriate disciplinary measures. The consequences must be consistent and well-communicated. A disciplinary policy detailing transgression mechanisms must be accessible to all staff.
7. Respond Fast and Take Corrective Action
Prompt responses and corrective actions address ineffective policies, compliance violations or data breaches. Quick correction of identified issues can prevent penalties or legal action. Corrective actions may include disciplinary action, overpayment recovery or policy updates.
8. Stay Informed About Regulatory Updates
Keeping updated on the latest trends and changes helps keep your organization compliant.
Several tips to stay informed include:
- Subscribe to regulatory body newsletters, like the HIPAA Journal, or set up Google Alerts for specific regulations.
- Network with industry professionals at conferences, webinars or on social media platforms.
- Consult with compliance experts, whether internal or external.
- Leverage technology such as Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) or data security tools.
Why Trust ProspHire for Healthcare Regulatory Compliance?
ProspHire's sole focus is healthcare. Since 2015, we have built a team of experts experienced in both public and private healthcare. With our extensive industry knowledge, we help our healthcare clients meet regulatory changes. Our areas of expertise include Medicaid practice, ACA planning, dental practice management and Stars performance improvement.
A recent example illustrates our compliance expertise. A large Pennsylvania managed care organization (MCO) had to achieve CMS document compliance. ProspHire assessed existing processes, established formal governance and implemented an operating model. We developed a Required Documents Program and Program Toolkit that defined processes. The result? The client achieved document compliance, saved costs and satisfied members.
Let ProspHire Help You Meet Regulatory Requirements
Healthcare organizations can find it challenging to stay updated with changing regulations. At ProspHire, healthcare is our passion. Our team anticipates healthcare regulation changes to offer effective compliance strategies. We customize our solutions to meet your organization's unique needs.
There's a reason ProspHire has appeared on Inc. Magazine’s annual list of America’s Fastest-Growing Private Companies five years in a row. Our people-first culture and exceptional customer service drive our continuous growth.
Let's talk about how ProspHire can help your healthcare organization navigate regulatory changes. Contact us today to learn more.

© 2025 ProspHire, LLC. All Rights Reserved / Terms of Use / Privacy Policy